The melting and freezing point changes with pressure but normally they are given at 1 atm. A solution will have a lower freezing point than a pure solvent.
13 Zeilen Boiling and freezing points of glycerine aqueous solutions.

Boiling and freezing points. All this is in the Science and Literacy Boiling and Freezing Melting Point. The melting point for water is 0 degrees C 32 degrees F. Freezing point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a solid.
1385 Δ T f T f 0 T f. Complete the second column of the Word Wall Builder Chart. Changes in boiling and freezing points of ionic solutions are based on.
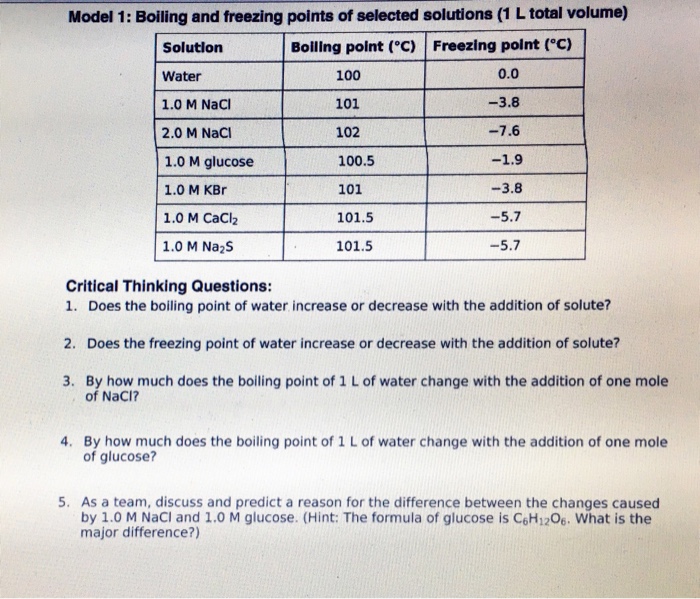
A solution has a boiling point and a melting point different from the normal values but the normal values themselves remain at 0 and 100. The number of total particles dissolved in the solvent. A demonstration of freezing and boiling points and standard measurements of temperature.
Given the K f for water is 186Cm a 22 m solution of glucose will have a freezing point of. The boiling points of glycerine. The first two physical properties we will cover are boiling and freezing point the point at which a substance turns into a gas and the point at which it tu.
The boiling point of water varies at various locations. The normal boiling point of water is 100 C and the normal freezing point of water is 0 C. Science Clips Keeping Warm.
Once the liquid starts to boil the temperature remains constant until all of the liquid has been converted to a gas. The effect of adding a solute to a solvent has the opposite effect on the freezing point of a solution as it does on the boiling point. The freezing point is the temperature at which the liquid changes to a solid.
Also to know is what is boiling and freezing point. Science and Literacy Boiling and Freezing Melting Point. Oh Boil the Pressure students make water freeze at 50 degrees Celsius.
When a liquid is heated it eventually reaches a temperature at which the vapor pressure is large enough that bubbles form inside the body of the liquid. When a liquid becomes a gas. You may have heard that water always boils at 100C but this is not completely true.
Boiling point and freezing point Addition of solute to form a solution stabilizes the solvent in the liquid phase and lowers the solvent chemical potential so that solvent molecules have less tendency to move to the gas or solid phases. All Hail the Freezing Point students flash freeze a test tube of water. Students drop a small piece of ice into a super-cooled water test tube and the entire test tube freezes instantaneously.
For pure compounds the following definitions can be given. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. When the opposite happens and a liquid turns into a solid it is called freezing.
Please select an option. This temperature is called the boiling point. This clip is from.
Wednesday Students will complete a summary writing with key terms from Tuesdays reading. By analogy to our treatment of boiling point elevationthe freezing point depression Δ T f is defined as the difference between the freezing point of the pure solvent and the freezing point of the solution. 21 Zeilen Boiling point C K b Cmolkg Freezing point C K f Cmolkg Data.
On Day 1 this lesson. At at high altitudes the lower pressure makes the boiling point several degrees lower. For pure water the boiling point is 100 degrees Celsius 212 Fahrenheit at one atmosphere of pressure and the melting point is 0 degrees Celsius 32 degrees Fahrenheit at one atmosphere of pressure.
Antifreeze is basically an additive that when added to water-based fluid reduces the freezing point. Boiling point of Water.
ads
