The boiling point of a liquid is a characteristic property and can be treated as criteria for the purity of liquid. These are the colligative properties that depends only on the no.
 Temperature And Temperature Scales Chemistry For Non Majors
Temperature And Temperature Scales Chemistry For Non Majors
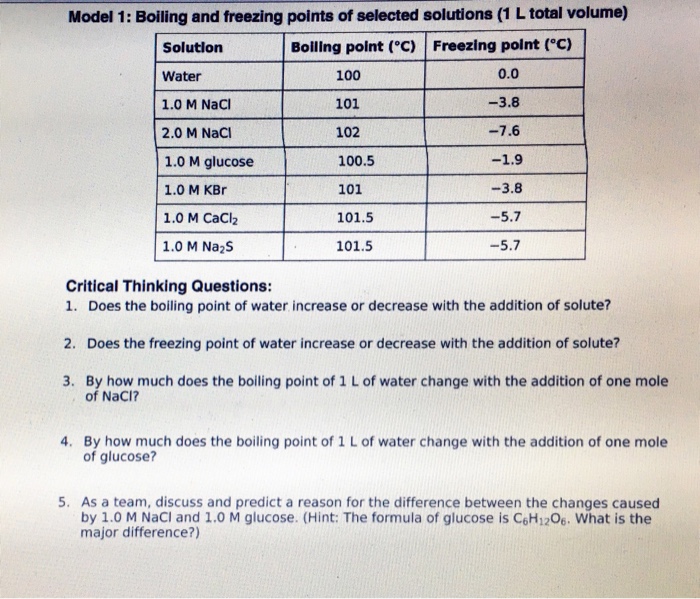
A solute lowers the freezing point of a solvent.
Boiling point and freezing point. 2 The depression in freezing point and the elevation in boiling point increases with increase in the concentration of the solute or impurity ie. Boiling Point and Freezing Point. The normal boiling point of water is 100 o C because this is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of water is 760 mmHg or 1 atm.
This week we will be identifying the boiling point of water and the freezing melting point of water. In fact as the boiling point of a solvent increases its freezing point decreases. September 11 2014.
Similarly freezing point depression is the lowering of a solvents freezing point due to the addition of a solute. Boiling Point of solution normal boiling point of solvent ΔT b. The freezing point is lowered while the boiling point is raised.
One may also ask what is melting point boiling point and freezing point. I cant tell you how surprised I was the first time I boiled water for my fifth graders. The boiling point is the temperature at which a material changes from a liquid to a gas boils while the melting point is the temperature at which a material changes from a solid to a liquid melts.
Of moles of the solute. ΔT f -K f m ΔT f the amount by which the freezing point is lowered. In dilute solutions the freezing point depression is proportional to the molality of the solute particles.
Boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure. Consequently measuring one of these properties for a solution prepared using a known mass of solute permits determination of the solutes molar mass. At at high altitudes the lower pressure makes the boiling point several degrees lower.
Increasing the glycerine concentration above 667 will increase the freezing point as indicated below. Glycerine to Water Concentration. The first two physical properties we will cover are boiling and freezing point the point at which a substance turns into a gas and the point at which it tu.
The bag of the salt became colder so the mixture froze faster. Boiling Point of a Liquid. The boiling points of glycerine also called glycerin or glycerol water mixtures are reduced with increased amounts of glycerine.
Generally there are three states of an object. The freezing points are reduced until glycerine concentration is 667 mass. For pure water the boiling point is 100 degrees Celsius 212 Fahrenheit at one atmosphere of pressure and the melting point is 0 degrees Celsius 32 degrees Fahrenheit at one atmosphere of pressure.
However the amount to which the boiling point increases or the freezing point decreases depends on the amount of solute that is added to the solvent. Keep in mind that a materials melting point is the same as its freezing point. Boiling water is no big deal to us grown-ups because we see it almost every time we cook.
Under normal conditions when the pressure of the atmosphere is approximately 760 mmHg water boils at 100 o C. Osmotic pressure and changes in freezing point boiling point and vapor pressure are directly proportional to the number of solute species present in a given amount of solution. The boiling point of a solution is higher than the boiling point of a pure solvent and the freezing point of a solution is lower than the freezing point of a pure solvent.
It increases with the increase in external pressure. Thus as solutes or solids are applied to liquids the freezing point drops and the boiling point rises. Boiling point elevation is the raising of a solvents boiling point due to the addition of a solute.
In principle the boiling-point elevation and the freezing-point depression could be used interchangeably for this purpose. 1 The impurities present in a liquid pull its two fixed points away from each other ie. The boiling point always occurs for a liquid it is the temperature at which the liquid.
Elevation of Boiling Point. Solid liquid and vapor. The freezing point of a pure solvent is lowered by the addition of a solute which is insoluble in the solid solvent and the measurement of this difference is called cryoscopyIt is found that Can also be written as Here K f is the cryoscopic constant equal to 186 C kgmol for the freezing point of water i is the van t Hoff factor and m the molality.
Since liquid salt decreases the freezing point of water the temperature of the bag of salt drops below zero degrees -1 degree Celsius. However the cryoscopic constant is larger than the ebullioscopic constant and the freezing point is often easier to measure with precision which means measurements using the freezing-point depression are more precise.
The melting and freezing point changes with pressure but normally they are given at 1 atm. A solution will have a lower freezing point than a pure solvent.
13 Zeilen Boiling and freezing points of glycerine aqueous solutions.

Boiling and freezing points. All this is in the Science and Literacy Boiling and Freezing Melting Point. The melting point for water is 0 degrees C 32 degrees F. Freezing point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a solid.
1385 Δ T f T f 0 T f. Complete the second column of the Word Wall Builder Chart. Changes in boiling and freezing points of ionic solutions are based on.
A solution has a boiling point and a melting point different from the normal values but the normal values themselves remain at 0 and 100. The number of total particles dissolved in the solvent. A demonstration of freezing and boiling points and standard measurements of temperature.
Given the K f for water is 186Cm a 22 m solution of glucose will have a freezing point of. The boiling points of glycerine. The first two physical properties we will cover are boiling and freezing point the point at which a substance turns into a gas and the point at which it tu.
The boiling point of water varies at various locations. The normal boiling point of water is 100 C and the normal freezing point of water is 0 C. Science Clips Keeping Warm.
Once the liquid starts to boil the temperature remains constant until all of the liquid has been converted to a gas. The effect of adding a solute to a solvent has the opposite effect on the freezing point of a solution as it does on the boiling point. The freezing point is the temperature at which the liquid changes to a solid.
Also to know is what is boiling and freezing point. Science and Literacy Boiling and Freezing Melting Point. Oh Boil the Pressure students make water freeze at 50 degrees Celsius.
When a liquid is heated it eventually reaches a temperature at which the vapor pressure is large enough that bubbles form inside the body of the liquid. When a liquid becomes a gas. You may have heard that water always boils at 100C but this is not completely true.
Boiling point and freezing point Addition of solute to form a solution stabilizes the solvent in the liquid phase and lowers the solvent chemical potential so that solvent molecules have less tendency to move to the gas or solid phases. All Hail the Freezing Point students flash freeze a test tube of water. Students drop a small piece of ice into a super-cooled water test tube and the entire test tube freezes instantaneously.
For pure compounds the following definitions can be given. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. When the opposite happens and a liquid turns into a solid it is called freezing.
Please select an option. This temperature is called the boiling point. This clip is from.
Wednesday Students will complete a summary writing with key terms from Tuesdays reading. By analogy to our treatment of boiling point elevationthe freezing point depression Δ T f is defined as the difference between the freezing point of the pure solvent and the freezing point of the solution. 21 Zeilen Boiling point C K b Cmolkg Freezing point C K f Cmolkg Data.
On Day 1 this lesson. At at high altitudes the lower pressure makes the boiling point several degrees lower. For pure water the boiling point is 100 degrees Celsius 212 Fahrenheit at one atmosphere of pressure and the melting point is 0 degrees Celsius 32 degrees Fahrenheit at one atmosphere of pressure.
Antifreeze is basically an additive that when added to water-based fluid reduces the freezing point. Boiling point of Water.
Typical radiator cap pressure is 12 to 16 psi. In the Fahrenheit scale water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees.
 The 5 Different Stages Of Boiling Water And How The Chinese Use Them F Golden Moon Tea
The 5 Different Stages Of Boiling Water And How The Chinese Use Them F Golden Moon Tea
However the value is not a constant.

What is boiling in fahrenheit. The simple answer to this question is that the boiling point of water is 100 C or 212 F at 1 atmosphere of pressure sea level. At sea level water has a range of 100 degrees in the Celsius scale from freezing point to boiling point with 0 being the freezing point and 100 being the boiling point. The correct answer is 212F.
When measuring temperature the usual units are Celsius degree Celsius or Fahrenheit degree Fahrenheit. Boiling Point - Celsius. Water boils at 3732 K Kelvin 100ºC Celsius or 212ºF Fahrenheit.
18 32. F C 95 32 Answer 212F. The boiling point of gasoline ranges between 104 and 392 degrees Fahrenheit.
This raises the boiling point of the engine coolant to about 250F to 260F. On the Fahrenheit scale however freezing is 32 degrees and boiling 212. Do 0 and 100 degrees Fahrenheit mean anything.
The boiling point of water depends on the atmospheric pressure which changes according to elevation. Absolute zero is defined as -45967F. Fahrenheit temperature scale scale based on 32 for the freezing point of water and 212 for the boiling point of water the interval between the two being divided into 180 equal parts.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply. How on earth were these numbers arrived at. Normally water boils at 212F.
Water boils at 100 C or 212 F at one atmosphere of pressure. However this range is not the same in the Fahrenheit scale. You can boil water at about 50 C in this system.
Liquids boil when the pressure of the atmosphere is equal to the pressure of the liquid. Also its helpful to keep in mind that the Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water where 0 C is the freezing point and 100 C is the boiling point. This the answer in F.
So to convert in fahrenheit just multiply the C temperature by 18. Everybody knows 0 degrees on the Celsius scale is the freezing point of water and 100 degrees is the boiling point. However when reporting temperatures in Kelvin we dont say degree Kelvin.
The IUPAC recommended standard boiling point of water at a standard pressure of 100 kPa 1 bar is. 22 rânduri Boiling Point - Fahrenheit. Definition of Fahrenheit and Celsius.
Normal body temperature is considered to be 986 F in real-life it fluctuates around this value. What is waters boiling point in Fahrenheit. There are two conventions regarding the standard boiling point of water.
When the pressure of the atmosphere is reduced a liquid boils at a lower temperature. The wide range of boiling points is due to the many different blends of components available to provide different characteristics such as higher octane lower fuel deposits and overall volatility. On the Fahrenheit scale water freezes at 32 F and boils at 212 F.
Conventionally the temperature at which water boils is 100 degrees Celsius or 212 Fahrenheit but only at sea level. Fahrenheit is a temperature scale named after the PolishGerman physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit 16861736 who proposed it in 1724. Your email address will not be published.
0 m 212 ºF. Add 32 to this number. Boiling and freezing point are therefore 180 degrees apart.
Boiling water is characterized by energetic bubbles and steam and it is considered to be hot. Boiling point of water is 100 C. In this scale the freezing point of water is 32 degrees Fahrenheit written 32 F and the boiling point is 212 degrees placing the boiling and freezing points of water exactly 180 degrees apart.
What is waters boiling point in Fahrenheit. However for every pound of pressure increase the boiling point goes up 3F. The normal boiling point is 9997 C 2119 F at a pressure of 1 atm ie 101325 kPa.
To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit you should multiply the figure by180 and then add 32 ie.
ads
