Structure of the Water Molecule Many of the physical and chemical properties of water are due to its structure. Water is a simple molecule consisting of one oxygen atom bonded to two different hydrogen atoms.
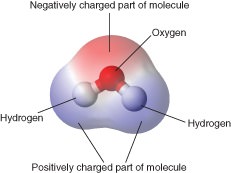
The polar ends of a water molecule are caused by the structure of the water molecule.
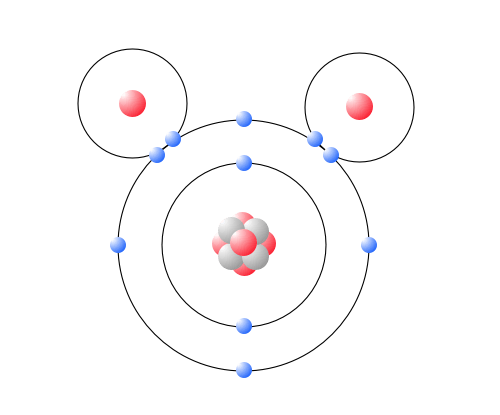
Describe the structure of a water molecule. Molecular Structure of Water. The atoms in the water molecule are arranged with the two HO bonds at an angle of about 105 rather than on directly opposite sides of the oxygen atom. Because of the higher electronegativity of the oxygen atom the bonds are polar covalent polar bonds.
Our cells are largely hydrologic and most body functions depend on water to work properly including respiration digestion and waste disposal. Its high electronegativity causes the oxygen atom to pull the shared pairs of electrons more towards itself. Nid191 view_modephoto_insert Water is a gtmoleculegt H2O that contains two hydrogen atoms each sharing a pair of electrons with an oxygen atom see Figure 1.
It covers over 70 of the earths surface and makes up as much as 95 of the living organisms. Virtually all life depends on the water molecule. Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen being only second to fluorine in its electronegativity.
Water H 2 O essentially considered one of the most important substances found on the earth. Describe the structure of a water molecule Program 1. 3 atoms are required to form a molecule.
Structure of water molecule is made up of one molecule of oxygen and two molecules of hydrogen bonded covalently. What is the structure of a water molecule. 3When a pocket of air becomes full of water vapor clouds form droplets those flat bottoms are where vapor begins to condense into water droplets.
2structure in which a hydrogen atom is in a line between the oxygen atom on its own molecule and the oxygen on another molecule. Ice like all solids has a well-defined structure. Since the two O-H bonds in water.
Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - Structure Of Water Molecule. Asked Apr 3 2018 in Physics by Golu 106k points The structure of a water molecule is shown in figure 9-E1. In all forms water is a polar molecule with electron-poor hydrogen atoms and an electron-rich oxygen.
Although the water as a whole is electrically neutral it behaves as an electrical dipole. Water composes 70 of mammalian and human body structures. One end there are two hydrogen atoms and on the other end there is an oxygen atom.
Therefore the structure of water molecule is an angular or bent structure. The H-O-H angle is approximately 1045 degrees. Describe the polarity of a.
Find the distance of the centre of mass of the molecule from the centre of the oxygen atom. Some of the worksheets for this concept are Chemistry of water work Water molecule structure Lesson 6 water structure properties time ii Model work teacher key Water structure and introductory article properties Chapter 15 work 3 the structural basis for Work 15 Model work student handout. Start studying The structure of a water molecule.
The Water H 2 O molecule has a triangular geometry with O-H bond distance of 00965nm and the H-O-H bond angle is 1045. The oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons of the covalent bonds to a significantly greater extent than the hydrogen atoms. Polarity of water molecule.
The structure of water varies considerably depending on its physical state. When atoms share electrons in this way a gtcovalent bondgt is created. As a result the O-H bond acquires polarity.
The three atoms make an angle. A water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Each water molecule is surrounded by four neighboring H 2 Os.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Water in the gas phase consists of isolated molecules of H 2 O. Each molecule is bent with a bond angle.
The center of each hydrogen atom is approximately 00957 nm from the center of the oxygen atom. It is this that leads to the hydrogen bonding interaction between water molecules. Water is a simple molecule consisting of one oxygen atom bonded to two different hydrogen atoms.
The oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons of the covalent bonds to a significantly greater extent than the hydrogen atoms. The structure of a water molecule is shown in figure 9-E1 Prev Question Next Question 0 votes. Two of these are hydrogen-bonded to the oxygen atom on the central H 2 O molecule and each of the two hydrogen atoms is similarly bonded to another neighboring H 2 O.
Because of the higher electronegativity of the oxygen atom the bonds are polar covalent polar bonds.
ads
